About CPAD
The California Protected Areas Database (CPAD) contains GIS data about lands that are owned in fee and protected for open space purposes by over 1,000 public agencies or non-profit organizations.
CPAD Includes:
- National/state/regional parks, forests, preserves, and wildlife areas
- Large and small urban parks that are mainly open space (as opposed to recreational facility structures)
- Land trust preserves
- Special district open space lands (watershed, recreation, etc.) and other types of open space
CPAD Does Not Include:
- Military lands used primarily for military purposes
- Tribal lands
- Private golf courses
- Public lands not intended for open space, such as municipal waste facilities, administrative buildings
CPAD Documentation
User Manual – Download the CPAD User Manual
Method for including GAP Codes in CPAD – Download
CPAD Structure
CPAD has three levels of data about protected lands:
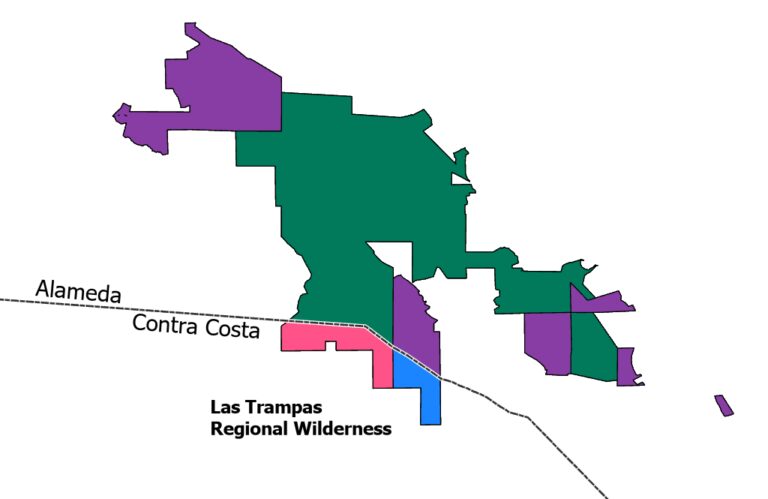
1. Holdings
The core element in the CPAD database is the Holdings, which have the most detailed attribute information in CPAD. Holdings are equivalent to assessor parcels, however CPAD holdings may not fully align with such parcels.
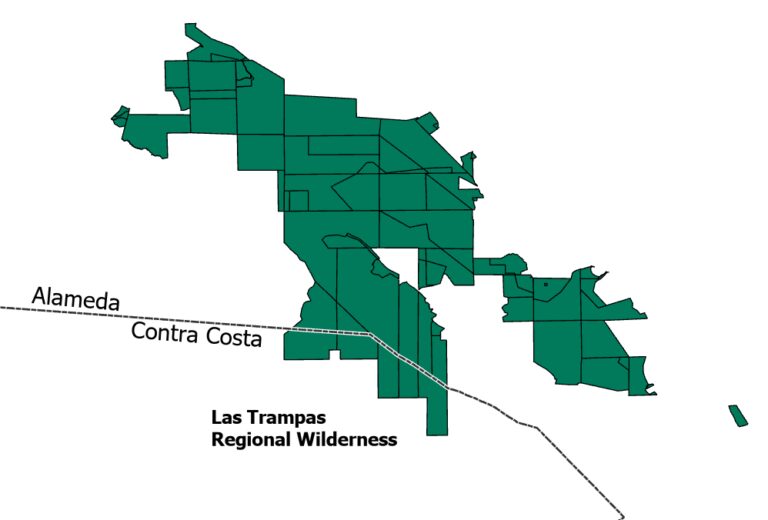
2. Units
Commonly named and owned protected areas within a single county (e.g., “Mt. Diablo State Park”) are Units, which may be made up of two or more Holdings. A unit may also have just one holding (e.g., an urban park, or another single parcel protected area). Units have summary attribute information. Commonly owned holdings that have different access attributes are defined as different Units.
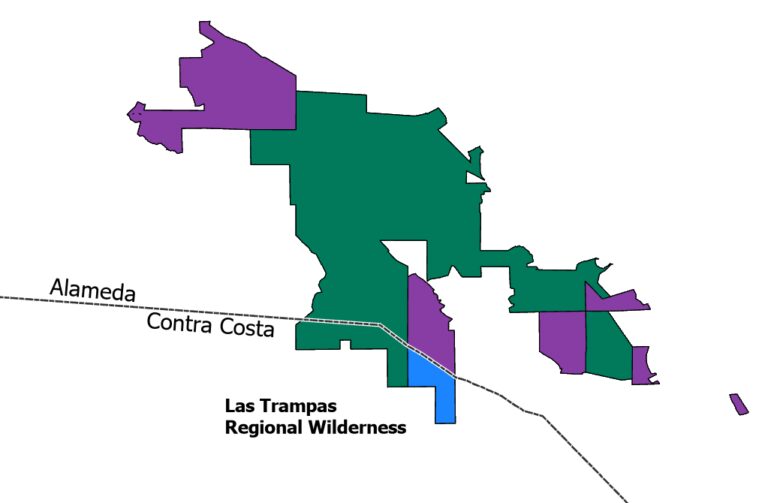
3. Super Units
Super Units are defined for use as cartographic aids (they show the outer boundary of groups of holdings, that have same name, manager, and access, regardless of county), as well as to support application developers working on recreational access projects that focus on knowing who manages sites.